Introduction
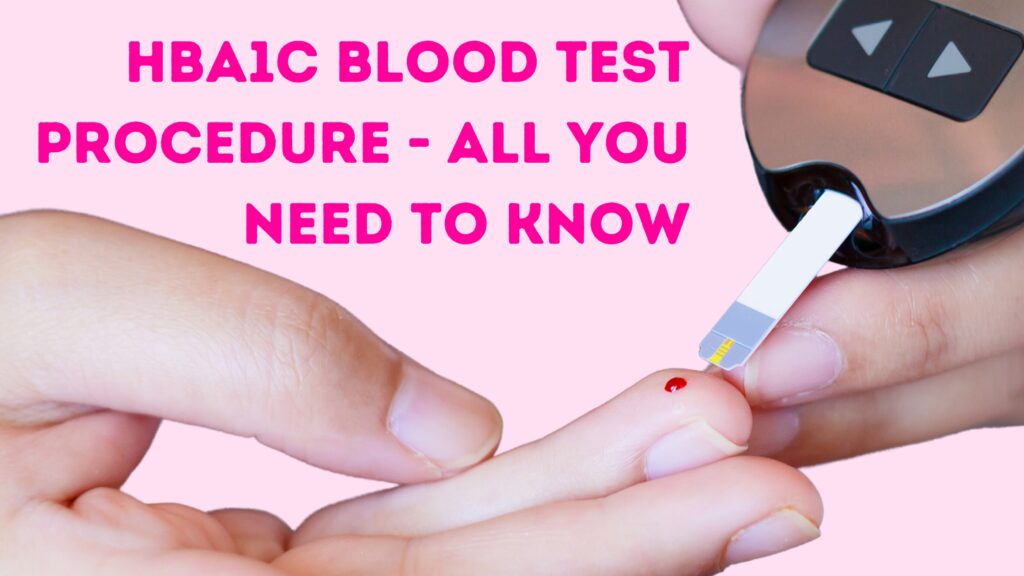
The Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) blood test, is also known as glycated hemoglobin. A person’s typical blood sugar levels over the previous two to three months can be estimated using the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). It is generally used to monitor, identify, and evaluate the management of diabetes. Here in this blog, we will describe the detailed procedure of HbA1c.
Preparation:
Generally, you don’t need to fast before an HbA1c test. The test can be performed at any time of day, with or without eating.
Blood Sample Collection:
The blood test will be conducted by healthcare specialists, generally a nurse or phlebotomist.
They will use antibiotic wipes to clean a small area of your arm.
They could collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm with a small needle, typically from the inside of your elbow.
Blood sample analysis
The sample collected of blood is sent to a laboratory for examination.
At the lab lab technicians will proceed to separate the hemoglobin A1c from the rest of the blood elements.
HbA1c Measurement:
To measure HbA1c levels in your blood, the laboratory uses specific techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or immunoassays. The results are shown in the percentage of total hemoglobin. A typical HbA1clevel for people without diabetes is 4% to 5.6%. This level is usually below 7% in those with well-managed diabetes.
Interpretation:
To measure HbA1c levels in your blood, the laboratory uses specific techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or immunoassays. The results are shown in the percentage of total hemoglobin. A typical HbA1c level for people without diabetes is 4% to 5.6%. This level is usually below 7% in those with well-managed diabetes.
Follow-Up and Treatment Adjustment:
Your healthcare practitioner might suggest changing your diabetes treatment strategy based on your HbA1c levels, such as changing your diet, using different medication or boosting your physical activity. You may need to schedule regular follow-up HbA1c tests to monitor your progress and make further treatment modifications.
Discussing Results:
Your medical expert will discuss your HbA1c results with you and, if required, provide suggestions on how to improve blood sugar control.
They might also talk about altering your diet, using different medications, and keeping an eye out for diabetes-related problems.
The HbA1c blood test is a crucial diabetes diagnosis and treatment tool. It provides a long-term perspective on blood sugar control and supports individuals with diabetes in making judgments about their treatments and way of living.
Conclusion
Ultimately, HbA1c blood tests are indispensable because they provide a comprehensive assessment of a person’s blood sugar control. It determines the chances of complications, assists in the evaluation and management of diabetes, and gives people with diabetes tools to take control of their health. Diabetes treatment involves routine HbA1c monitoring, which can help diabetics achieve better results and better outcomes.