The thyroid gland, a tiny, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, controls the body’s metabolism and affects almost every bodily function. Thyroid issues are unfortunately quite frequent, particularly in women.
Women are more susceptible to thyroid problems than men, with a five to eight times higher risk. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms of thyroid problems in women is imperative for prompt diagnosis and efficient treatment.
This article will discuss the symptoms of thyroid problems in women, including the various causes.
What is Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that prevents your thyroid gland from making enough hormones. Your thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that keep your body functioning normally.
When the thyroid produces too much thyroid hormone, your body consumes energy faster. Quick energy usage makes you tired and can increase your heart beat rate, cause weight loss without effort, and sometimes make you feel nervous. This condition is called hyperthyroidism.
It is also possible that your thyroid makes too little thyroid hormone. This is known as hypothyroidism. Too little thyroid hormone in the body can result in fatigue and weight gain and even make you sensitive to cold temperatures.
What Causes Thyroid Disease?
The two primary types of thyroid disease are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, caused by other diseases influencing the functioning of the thyroid gland.

Causes of Hypothyroidism
Conditions that may lead to hypothyroidism include:
- Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland. It has the potential to decrease the production of thyroid hormones.
- Postpartum thyroiditis: After giving birth, some women may experience an autoimmune condition called postpartum thyroiditis, which can cause temporary hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
- Iodine deficiency: The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce hormones, and a deficiency of this mineral affects millions of people worldwide.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune thyroid disease that causes inflammation and damage to the thyroid gland.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Conditions that may lead to hyperthyroidism:
- Graves’ disease: This condition can make the entire thyroid gland overactive and produce large amounts of hormones.
- Nodules: Overactive nodules within the thyroid gland can also lead to hyperthyroidism. When there is a single nodule in the thyroid gland, it is referred to as a toxic autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. In contrast, a gland that has multiple nodules is known as a toxic multinodular goiter.
- Excessive iodine: Your thyroid gland may produce more hormones than necessary if there is an excessive amount of iodine in your body, which is essential for producing thyroid hormones.
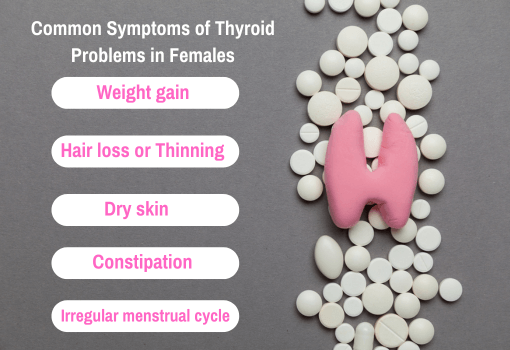
Common Symptoms of Thyroid Problems in Females
The most common thyroid issues come with hypothyroidism. The hypothyroidism symptoms in females include the following:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Increased sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Hair loss or thinning
- Dry skin
- Constipation
- Irregular menstrual cycle changes
Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Increased feelings of anxiety
Conclusion
In conclusion, thyroid disease influences your thyroid gland and does not let it produce the proper amount of hormones. It is more common in women, unlike men, especially women in their thirties.
Not treating a thyroid condition can significantly burden your other organs, particularly your heart. Additionally, experiencing the symptoms of an imbalanced thyroid can be extremely unpleasant.
Therefore, it is important to stay on top of whatever thyroid symptoms you experience. If you are interested in getting your thyroid levels tested, we at Grace Laboratory would be happy to assist you.
FAQs
1. How to control thyroid in females?
An effective way to control thyroid in women is incorporating Vitamin A into a daily routine. The most common Vitamin A-rich foods include yellow and green veggies, carrots, eggs, apricots, spinach, and carrots.
2. Are overactive thyroid and hyperthyroidism the same thing?
Yes, “overactive thyroid” and “hyperthyroidism” are the same. Both terms describe a condition in which the thyroid gland generates excessive thyroid hormone, causing various symptoms connected to the body’s metabolic rate.
3. What are the different types of thyroid tests?
The different thyroid tests include TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), Free T4 (thyroxine), Free T3 (triiodothyronine), and thyroid antibody tests, among others.
Also Read: Thyroid Blood Test Rules